URBAN PLANNING AND ECONOMY AFTER BOYCOTTING CHINA PRODUCTS IN INDIA
China–India
relations, also called Sino-Indo relations or Indian-Chinese
relations, refers to the bilateral relationship between China and India. Although the relationship
has been cordial, there have been border disputes. China and India are the
two most populous countries and fastest growing major economies
in the world. Growth in diplomatic and economic influence has increased the
significance of their bilateral relationship. Bilateral trade between China and
India touched US$89.6 billion in 2017–18, with the trade deficit widening
to US$62.9 billion in China's favour. In 2017, the volume of bilateral
trade between India & China stands at US$84.5 billion. Chinese exports to
India amounted to $58.4 billion or 2.3% of its overall exports, and 12.6% of
India's overall imports in 2014. The 10 major commodities exported from China
to India are Electronic equipment ($16 billion), Machines, engines, pumps ($9.8
billion), Organic chemicals($6.3 billion), Fertilizers($2.7 billion), Iron and
steel($2.3 billion), Plastics($1.7 billion), Iron or steel products($1.4
billion), Gems, precious metals, coins($1.3 billion), Ships, boats($1.3 billion),
Medical, technical equipment($1.2 billion).
On
10 May 2020, Chinese and Indian troops clashed in Nathu La, Sikkim, leaving 11
soldiers injured. Following the skirmishes in Sikkim, tensions between the two
countries grew in Ladakh with a build-up of troops at multiple locations. 20
Indian and 43 PLA soldiers were reportedly killed in action on
the night of 15/16 June. Following the Galwan Valley clash on 15 June 2020,
there were renewed calls across India to boycott
Chinese goods. The question may arise that what may
the role of urban planning after boycotting the China products in India? and
how the India can become self-reliant and revive its economy after boycotting
China products? This question will be answered with the solutions in next five
points and strategies,
1) Special Economic
Zones: In India there are total 238 SEZs present in various state. A Special
economic zone (SEZ) is an area in which the business and trade
laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are located within a
country's national borders, and their aims include increased trade balance,
employment, increased investment, job creation and effective
administration. The creation of special economic zones by the host country
may be motivated by the desire to attract foreign
direct investment (FDI). The benefits a company
gains by being in a special economic zone may mean that it can produce and
trade goods at
a lower price, aimed at being globally competitive. The Government and Planners
need to focus on creating the SEZs in order to boost the trade activities,
investment in business and increase employment opportunities. The policies may
be created to attract foreign companies for direct investment and manufacture
the products completely in India with some reliefs in taxes. This is possible
by creating Foreign-trade zone (FTZ) which is a class of special
economic zone. It is a geographic area
where goods may be landed, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and
re-exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject to
customs duty. Free trade zones
are generally organized around major seaports, international
airports, and national frontiers areas with many geographic
advantages for trade. Free economic zones need to adopted which is a class
of special
economic zone (SEZ) designated by the trade and
commerce administrations of various countries. The term is used to designate
areas in which companies are taxed very lightly or not at all to encourage
economic activity. This zone will attract businessman, companies to invest
and start manufacturing the products that will be completely made in India and
will be an important step in self-reliant programme of India. Creating SEZs
will also help to solve the problem of lack of infrastructure in India. This
step will lead to creation of more employment opportunities and will help to
revive the economy of India.
2) Urban Haats: The scheme for
establishing Urban haats was introduced by Ministry of Textiles, GoI. The
objective of the scheme is to setup a Infrastructure and Technology Support
permanent marketing infrastructure in big towns/ metropolitan cities to provide
direct marketing facilities to the handicraft’s artisans/handloom weavers. The
scheme is implemented through State Handicrafts/Handlooms Development
Corporations/Tourism Development Corporations/ Urban Local Bodies with
sufficient financial resources and organizational capacity to implement the
project. The planners need to focus on creating urban haats in cities so that
handicrafts artisans, handloom weavers, crockeries and toys manufacturer,
electronic equipment, iron and steel, machines, engines and pumps, dairy
products, snacks etc can do marketing, organise exhibition and
commercialization of products made in India and will encourage to manufacture
good and commodities at a large scale in India. Establishing urban haats will
help the citizens to know more about the local products and equipment’s made in
India. This will help to make citizens rely less on foreign products and use of
maximum products made in India. This action would lead to vocal for local. 'Vocal for local'
is the Indian Prime Minster, Narendra Modi's appeal to all the Indians to use
only Indian products an important strategy for self-reliant India.
3) Skilled Labours: The proportion of
formally skilled workers in India is extremely low, at 4.69% of
total workforce as of 2019. The labours are important assets for the production of goods and
services and India is lacking in having a skilled labour workforce. The
planners need to focus on making the policies programs and advising the
government to establish vocational training centre in cities/towns, where
companies from industries will be giving a training program for unskilled
labours for short span of time and making them liable to earn income and gain
employment opportunities. This program will help the industries to have a skilled labour
workforce and increase the percentage skilled labours in India. The lack of
skilled labour workforce signifies that the production and manufacturing of
good and services are limited and do not provide the quality required. So,
citizens rely more on the products manufactured in foreign countries. The
vocational training centres will help to increase in skilled labour workforce
in India and encourage the industries to manufacture the products at a faster
rate with quality improvisation in products. So that citizens can rely more on the
products Made in India. This intervention for labours will help to make
self-reliant program a grand success and achieving vocal for local.
4) "Make in India" is an initiative which
was launched on 25 September 2014 with three major objectives: (a)
to increase the manufacturing sector's growth rate to 12-14% per annum in order
to increase the sector's share in the economy; (b) to create 100 million
additional manufacturing jobs in the economy by 2025; and (c) to ensure that
the manufacturing sector's contribution to GDP is increased to 25% by 2025. The
policy approach was to create a conducive environment for investments, develop
modern and efficient infrastructure, and open up new sectors for foreign
capital. India jumped to 63rd place out of 190 countries in the world Banks'
2019 Ease of Doing Business Index from 130th in 2016. The planners need to
focus on adopting the policies to encourage the engineers for complete
manufacturing of the electronic equipment and attract foreign companies in
India itself rather than relying on importing different parts from China. India
is dependent on 90% of raw material from China required to manufacture
medicines. There is need to change these mindsets and need to adopt the
policies/schemes that will encourage the Indian and attract foreign pharmaceuticals
companies to produce raw material in India itself required to manufacture
medicines as a bilateral trade. India ranks 63rd in ease of doing
business the reason is expensive land and lack of infrastructure. The planners
need to focus on fulfilling the lack in infrastructure through development
plans, regional plans and local area plans of cities/towns. The government need
to focus on adopting the polices that will make the land values low for
investment in the manufacturing sector that will increase the ease of doing
business. Doing this will help to manufacture each and every product, goods,
equipment in India itself rather than relying on China. Planners need to go for
cluster development. Suppose the construction is going in particular area and
material required is imported from different states and countries, but in
cluster development all the material required for construction, manufacturing
purpose will be made available in the cluster itself. This will foster the
development process and fulfil the lack in infrastructure at a faster rate.
Make in India initiative will help to boost manufacturing sector at a large
scale. This initiative will help to grow business sector at a faster rate and
encourage to make products in India itself. This will be a step towards
self-reliant program of India.
5) Smart Industrial Cities: Planners
need to go for the greenfield smart industrial cities like AURIC industrial
city located in Aurangabad, Maharashtra with the use technology for
infrastructure upgradation. The smart industrial cities need to be equipped
with infrastructure for industrial usage with main focus on textile, food,
defence, engineering, automobile and electronics etc. The intention of creating
smart industrial cities should also be focused on residential, commercial and
other purposes with 60:40 percentage. The planned smart industrial townships
will act as an investment node. Also, this city will fulfil the infrastructure,
housing, income, employment and basic amenities requirement. This city will prove
as a financial hub with focus on manufacturing and business sector and
encourage to make good and commodities in India itself. This will make sure the
less dependence on China to import the commodities required to manufacture
products in India. Else it may increase the percentage of export of goods
manufacture in India to other countries. This initiation will help to revive
economy of India after boycotting China products.
Adopting this
strategies will definitely help to achieve the five pillars of Atmanirbhar
Bharat Abhiyaan (self-reliant program of India)
like an economy that takes quantum jumps and not incremental
change, infrastructure should be world class and fulfil the identity of India
which is synonymous with modern India, a system that is based on technology
driven arrangements fulfilling the dreams of the 21st Century not
the policy of past century, a vibrant demography which is the source of energy
for a self-reliant India and demand, whereby
the strength of our demand supply should be utilized to a full capacity.
If a soldier can sacrifice their life for safety and security of the country,
then why not all the planners comes together and take a pledge and commit to
make India a developed country and leading economy in the world. If all
planners, bureaucrats, experts, youths, engineers and scientists unite and
decide to make India a self- reliant India, then why else need to rely on
foreign countries products and we can achieve the strategy vocal for local and
be self-independent.
Together we will build,
Together we will grow
Related Articles

Indian village – The Unknown Strengths

PLANNING IN INDIA
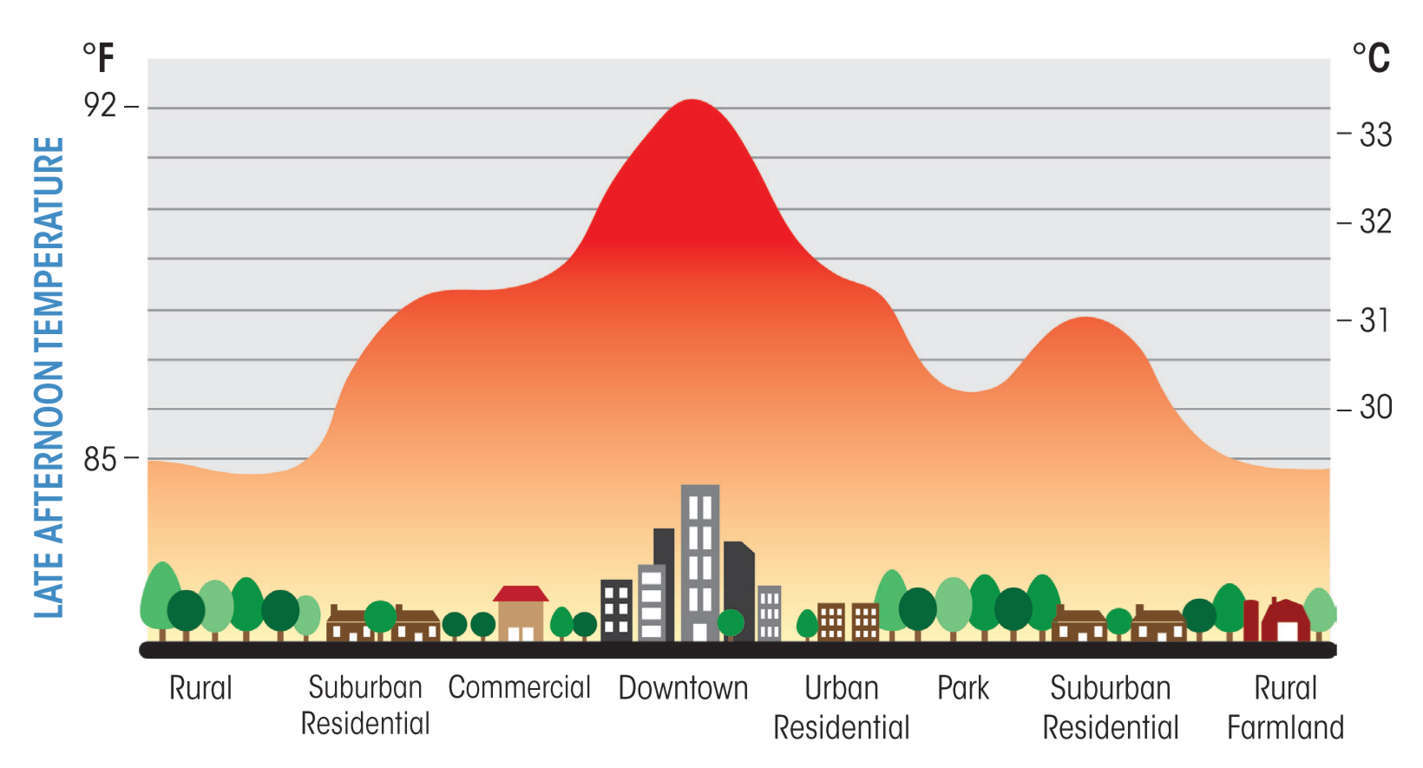
URBAN HEAT ISLAND INNOVATIVE WAY TO REDUCE ITS EFFECT

LIVEABLE CITIES





