Housing Typologies and Characteristics
Introduction
Housing is the most vital and basic necessity of human being. Housing allows social security and safety to the households, resulting in better quality of life and welfare of the society. The term housing brings out physical as well as social structures in which an interconnected system of relationship can be observed. According to Census of India, there are various housing characteristics to understand the housing situations. They can be classified as:
- Housing condition is a primary housing characteristic which determines the quality of houses based on good, dilapidated and livable conditions.
- Housing tenure status is the ownership of housing which reflects on economic composition and dependency. The tenure status is sub-categorized into owned, rented and any other types.
- Housing structure can be studied through permanent, semi-permanent and temporary structures based on the types of materials used for wall, roof and floors.
Housing Typologies
The
typologies associated with housing can be divided as formal housing and
informal housing. In case of formal housing there are private, public, rental
and cooperative types of housing.
- Private
housing – Private housing is an individual effort giving preferences for
personalized needs.
- Public
housing – Usually, a public housing is a government initiative which offers
shelter for all through various housing programs and projects.
- Rental
housing – A type of housing where housing access is provided to the people who
are not able to afford housed of their own.
- Co-operative
housing - Co-operative housing aims at
developing housing through various co –operatives for funding needs.
Informal
housing can be descried as unhealthy settlements that are created due to lack
of economic instability. They are usually located on the peri- urban areas or
at the inner most areas of the city. Informal housing lacks basic amenities and
utilities provided for a living. Some of the examples included in informal
housing are notified and non-notified slums, squatters, pavement dwellers and
other illegal dwellers.
The
differences in formal and informal housing are determined through housing
stocks and housing analysis of gap assessments. Housing shortages are
households living in factors such as obsolescence, congestion and homelessness
conditions.
Concepts and principles of neighborhood
The term
neighborhood can be defined as an area where a group of people live together,
with respect to the size of the group results in the creation of villages,
towns or cities. A neighborhood unit is described as a planned unit where
people live in larger area with all basic facilities available at a walkable
distance.
According
to Clarence A. Perry a New York planner, neighborhood concept is an
arrangement of 5000 – 9000 people supporting an elementary school of student
population of 1000 - 1200. The total area for a neighborhood would be 160 acre
with a population density of 10 houses per acre. And the shape of the area is
in such a way that the school students need not move more than one - quarter
mile to reach the school. There would be a 10% of area allotted for
recreational purposes. And the area would also be implemented with shopping
centers, community spaces and religious areas.
Clarence
A. Perry’s Neighborhood Unit of 1929
Source:
Neighborhood Unit and its Conceptualization in the Contemporary Urban Context
There are six basic principles of
neighborhood unit concept. They are:
- Arterial streets are placed along the boundaries
of the neighborhood, not through the residential area of the neighborhood.
- The internal streets should be designed according
to the use cul-de-sac (dead ends) for avoiding high traffic and providing
peaceful environment.
- The total population of the neighborhood should
be in a way supporting the requirement of elementary school.
- The elementary should be located at the center of
the neighborhood unit.
- The radius of neighborhood should be maximum one quarter mile, thus limiting the movement of school student to that distance.
- Shopping centers are provided at the edges of the neighborhood and preferably at the cross section of the major streets.
Residential Densities
The basic
measurement for determining physical characteristics of the area is known as
density. Densities differ based on the number of units such as population,
dwelling units, in the given area. Residential density is based on three
elements units to be measurement, area for the unit measurement, land which can
be excluded / included in the given area. Among these the land factor is the
most important factor which causes the greater variations in the residential
density.
Residential
density helps us to understand the intensity of the development of an area.
There are two important types of residential densities; one is the Net Residential
Density which is the dwelling unit count upon area with residential use and
Gross Residential Density can be referred as dwelling unit upon residential
area including other land use areas. Apart from providing physical
characteristics, residential densities associate economic and social
characteristics.
Affordable housing
Affordable
housing is housing that are reasonable for the lower income groups. It aims to
meet the housing needs of various income categories such as lower, middle and
economically weaker sections of society without compromising on the quality of
housing. President of Confederation of Real Estate Developers Association of
India (CREDAI) Satish Magar defined affordable housing as “units with a carpet
area as defined under RERA that do not exceed sixty square meters in the metros
and 90 square meters elsewhere''.
People
live in unauthorized spaces not by choice but circumstance which makes it
affordable to them. In India, affordability plans are implemented through
government policies, schemes such as Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY), NTR
Housing and Rajiv Awas Yojana and public – private partnership to result in
better standard of living and creating social inclusions.
Affordable
housing is estimated through housing shortage, which can be calculated through
three factors such as obsolescence factor, congestion factor and homelessness.
Accessing these factors determines the existing housing shortages and thereby
providing affordable housing demand.
Real estate valuation
Real
estate is defined as the land along with any kind of structures which can be
organic or man built. There are six main types of real estate such as
agricultural real estate, residential real estate, commercial real estate,
industrial real estate, mixed use and special purpose like public and
semi-public uses.
There
exist physical as well as economic characteristics for real estate. Physical
characteristics include durability, heterogeneity and stability factors. While
economic characteristics marked as a source of income involves market value,
investment strategies and area of choice. Understanding these characteristics
develops standardized dealings of real estate.
The real
estate valuation is a process of determining the actual value of the land or
building for use or as an investment through various standards. There are
various factors taken into consideration while performing real estate valuation
such as land value in market, proximity of infrastructures, material used and
availability of amenities and utilities.
Related Articles

Integrated Urban Water Management
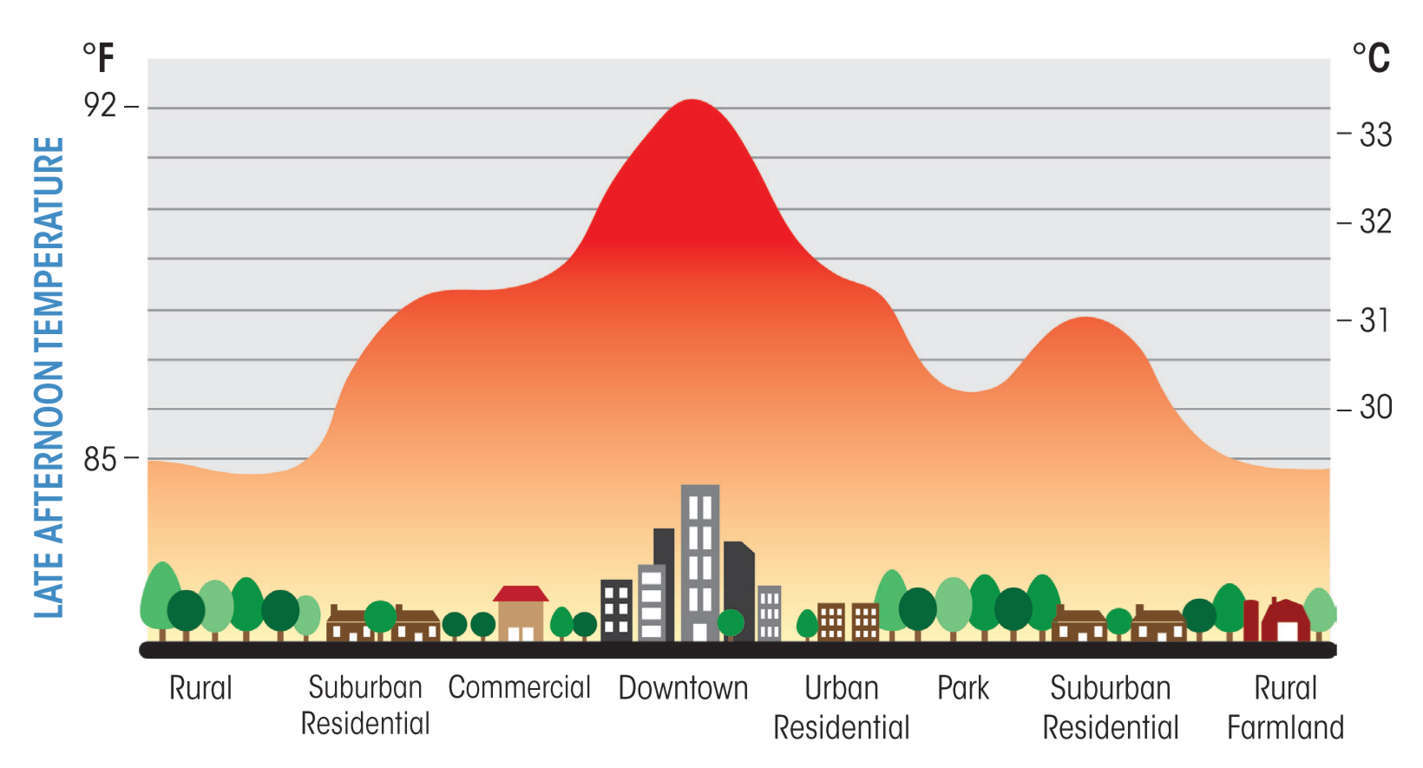
URBAN HEAT ISLAND INNOVATIVE WAY TO REDUCE ITS EFFECT
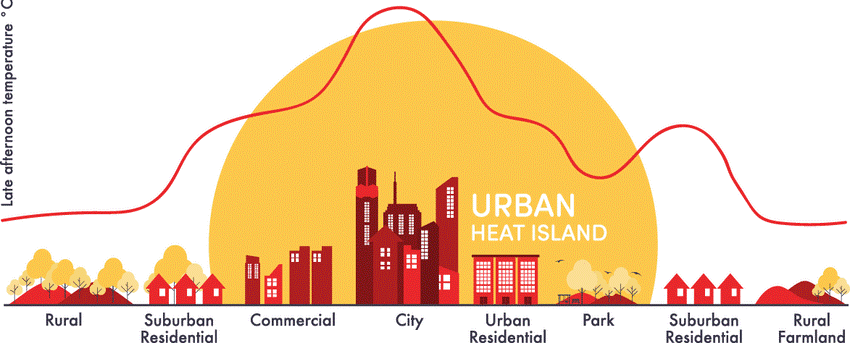
URBAN HEAT ISLANDS

URBAN AGRICULTURE: A STEP TOWARDS SUSTAINABILITY




