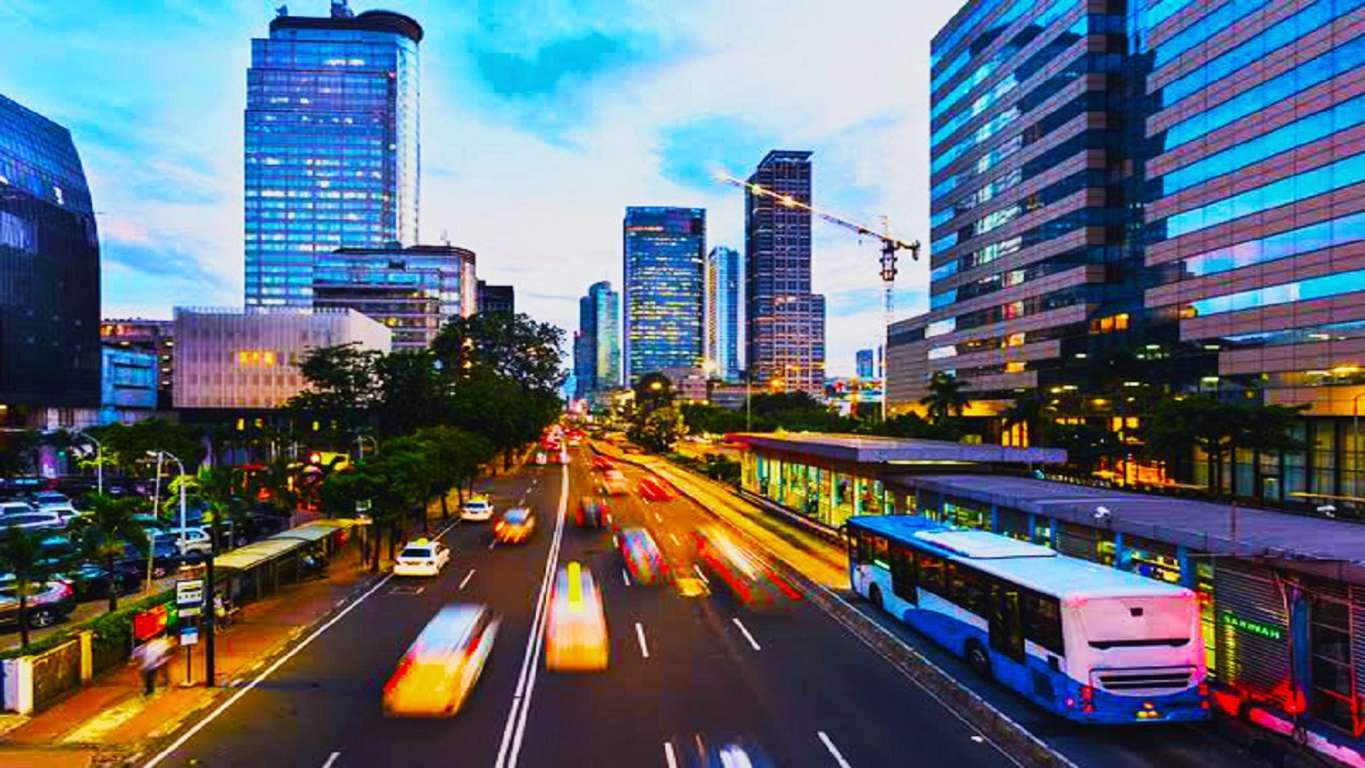
Urban Planning to get boosted by IOT
Urban
planning is an art of systematic arrangement and allocation of resources both
living and non-living for a sustained, synchronized and healthy living
environment. Post the beginning of industrialization, global community
acknowledged the importance of preserving the natural environment. Advent of
fossil fuel-based technologies, mining of minerals, manufacturing and service
industry catalyzed the exploitation of natural resources. Agriculture based
economies started migrating towards digitized economies. Population exploded,
people started migrating from rural areas towards urban areas in search of
better future and enhanced standard of living. Today, Japan depicts a perfect
Information Technology based model of an urban society that has evolved into a
world’s leading manufacturing hub.
Development
in computer science gradually after the 2nd world war has propelled
the expeditious growth with far greater accuracy and consistency in almost all
the spheres of life. With the invention of Internet technology by the US army,
world soon became connected into a loop of globalization. Today, we are living
in the age of information-based technology. We have numerous equipment and
devices that work on the basis of data being fed to them leading to the
automation many activities and replacement of human resource as a capital for a
better prospectus.
We
are slowly on the path of becoming a SMART society. SMART CITY, an initiative
by the Union Government under the leadership of PM Narendra Modi is an arduous
initiative to develop an all-inclusive and ecologically rich infrastructure
facility linked together via digital paraphernalia. India’s population
currently stands at 130 cr as per the last census conducted in 2010 and global
temperature is expected to rise by 3-4 degree centigrade by the end of this
century causing the icebergs to melt and submerge many of the coastal cities
like- Mumbai, Pondicherry, etc. Digital Technology based development and
settlement on the human population is the need of the hour.
IoT- Digital solutions are
faster and more accurate. Moreover, it provides the flexibility to be available
at any time and from any place even if the intervention is required at a place
located thousand of miles away. This IoT, i.e. Internet
of Things in the new future that can provide a
multitude of environment friendly and life sustaining opportunities in the near
future. Internet of Things, as the term suggests is an interconnected network
of objects both- connected locally and globally via any networking solution. Objects
can be- computers, smartphones, washing machines, microwave oven, light system,
etc. Networking can be in the form of- Bluetooth, internet, satellite
communication, RFID, etc. depending upon the volume of data and the speed with
which it is to be transferred or communicated.
IoT can be a boost to the ambitious Smart City Mission of India and a key platform for urban planners to improvise the information and communication technology in the development of living spaces. Some interesting developments which are already under use and can be further developed are-
1) Travel and Transportation- Connecting all the vehicles via GPS tracker and enabling the vehicle to automatically select the shortest and fastest route to reach the destination by feeding in the data. Self-driven cars are already under development from TESLA and GOOGLE. Thus, the problem to traffic jams and vehicular congestions can be eliminated. Also, dramatic reduction in the count of accidents.
2) Farming and Agriculture- Self-watering or regulated watering system for the public parks, lawns and trees can be a blessing to help both in the soil and water pollution. Sensors can detect the humidity content of the soil and forward the data to a centralized system, which on the basis of the re-decided data range can in turn command the irrigation system to release the designated amount of water. Thus, it can help reduce the wastage of water. Same can be done to maintain the pH level of the soil and aid in maintaining the soil fertility.
3) Disaster Management- via IoT can help save hundreds and thousands of lives. Imagine yourself enjoying a nap on a hot sultry noon of your most awaited Sunday and suddenly a massive fire breaks out due to a short circuit just on the floor above yours. You are unaware and continue to enjoy your nap. While, the occupant whose flat will be giving out flames and smoke is away for a movie with his family. Dreadful indeed! However, thanks to the sensors and alarm systems, as soon as the smoke and temperature rise is detected by the sensor, it sends the information to a central monitoring system of the facility management team of the society which cuts off the electricity supply, blow out the alarm and an automated speaker reads aloud fire fire, vacate the building. Thus, it ends up helping you save your life and property of your friend residing above.Similar, arrangements can safeguard a city against- floods, explosions, lightning attack, gas leakage.
4) Energy Management- Developing a centralized smart energy network can help conserve and price the energy demand in a realistic and sustainable style. Tracking the peak hours for energy consumption and areas of energy consumption is vital to allocate a more robust and cost-effective energy system. Enabling an automated energy delivery mechanism can track and check theft for energy and revenue collection which is a major block in energy sector of India. Connecting the individual household meter such that if the used load exceeds the sanctioned load or if the bill generated has not been paid by the due date, the connection can automatically get switched off from the central system and the same can be restored upon correction. This technology can be further used to capture the sustainable energy generation from- solar and wind in urban areas. The energy so generated both from public and personal properties can be connected on-grid and can reduce our dependence on fossil fuel and uranium-based energy sources.
5) Water supply and waste management- Water is an elixir of life. Installing sensors along the water bodies where sewage or industrial waste is dumped can help check the pollution level in the water bodies. Sensor will transmit the recorded observation to the system which will then monitor the permissible level of pollutants in the water from the source of pollution. If the data is found to disobey the permissible level strict penalty can be imposed on the concerned authority for not taking adequate precaution to check the pollutant discharge. We will have a reduced cost to purify the water and in case of receding water level or rising water level a signal sent off by the sensor can stimulate the system to regulate the permissible water level in the water body.
Please
note, these are very basic features that are being implemented in a fragmented
and a localized manner. We need a robust system that can perform holistically
to make a better use of the natural resources and be able to meet the demands
of the future generations without any shortage and toxicity.
Challenges-
- Large financial gap
between the existing rich and poor segment of the society. Will be a challenge
for government to bridge this gap to facilitate the digitization.
- Many
jobs will become redundant such as those of a- gardener, security guard,
electrician, plumber, etc. as major dependence will be upon the software
technology.
- Huge
capital investments are required and India is still a developing country.
- The
literacy level is also poor worsened by the existing inadequate and poor public
infrastructure which will demand complete renovation/ upgradation or
replacement.
- Political
uncertainty is high in India which may derail many proposed or approved
projects.
It is imperative upon us to take a collective responsibility and utilize even the slightest of opportunity to turn the tide in favor of a sustainable and nature friendly society.
By Nilay Singhal: "Nilay is a Civil Engineering pass out from Birla Institute of Technology and completed his MBA in Construction Project Management from RICS. He holds a keen interest in development issues for sustainable growth of the society. An admirer of nature, foodie and a passionate writer."
Related Articles
Sustainable Urbanism: Gap Between Policy and Reality
Transit Oriented Development as a Solution to Indian Cities

Urban Planning and Sociology
The philosophical approach through understanding the psychological needs of humans resulting in joyful spaces




